In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, the imperative for robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information is more pronounced than ever. Cybersecurity insurance has emerged as a critical component in the arsenal of tools that organizations employ to fortify their defenses against cyber threats. In addition to addressing immediate security concerns, effective cybersecurity insurance policies also play a vital role in mitigating financial losses and ensuring business continuity in the event of a cyber incident. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the definition, significance, and intricate implementation of cybersecurity insurance, including its integration with IT risk management strategies to safeguard organizational assets and reputation.
What is Cybersecurity Insurance?
Cybersecurity insurance, also referred to as cyber insurance or cyber liability insurance, represents a specialized policy meticulously designed to shield businesses from the financial fallout of cyber threats and data breaches. Unlike traditional insurance, it goes beyond conventional coverage, addressing the nuanced challenges posed by the continually evolving digital landscape.
The escalating frequency and sophistication of cyber-attacks underscore the pivotal role that cybersecurity insurance plays in an organization’s overarching risk management strategy. The financial implications of a breach can be staggering, encompassing legal expenses, notification costs, and potential regulatory fines.
In 2018, a major data breach rocked the hospitality industry, exposing the personal information of up to 500 million guests staying at Marriott hotels, primarily through the Starwood chain. Hackers exploited a compromised employee login to gain access to a treasure trove of data, including names, addresses, emails, phone numbers, passport numbers, and travel dates. While the company incurred significant costs, estimated at $28 million initially, including notification services, credit monitoring, legal fees, and other response measures, their robust cyber insurance played a crucial role in mitigating the financial blow to a mere $3 million.
Cybersecurity insurance has several benefits. It serves as a safety net, empowering businesses to navigate the tumultuous aftermath of a cyber incident with heightened resilience. This makes undergoing cybersecurity insurance costs rather logical for organizations.
Cybersecurity Threats Covered by Cybersecurity Insurance Providers
Cybersecurity insurance policies typically extend coverage to a spectrum of threats, including but not limited to data breaches, ransomware attacks, and denial-of-service incidents. A nuanced understanding of the specific threats covered is imperative for organizations to ensure a comprehensive shield against potential vulnerabilities.
The specific cybersecurity threats covered by insurance can vary significantly between policies and insurers, but some common areas of coverage include:
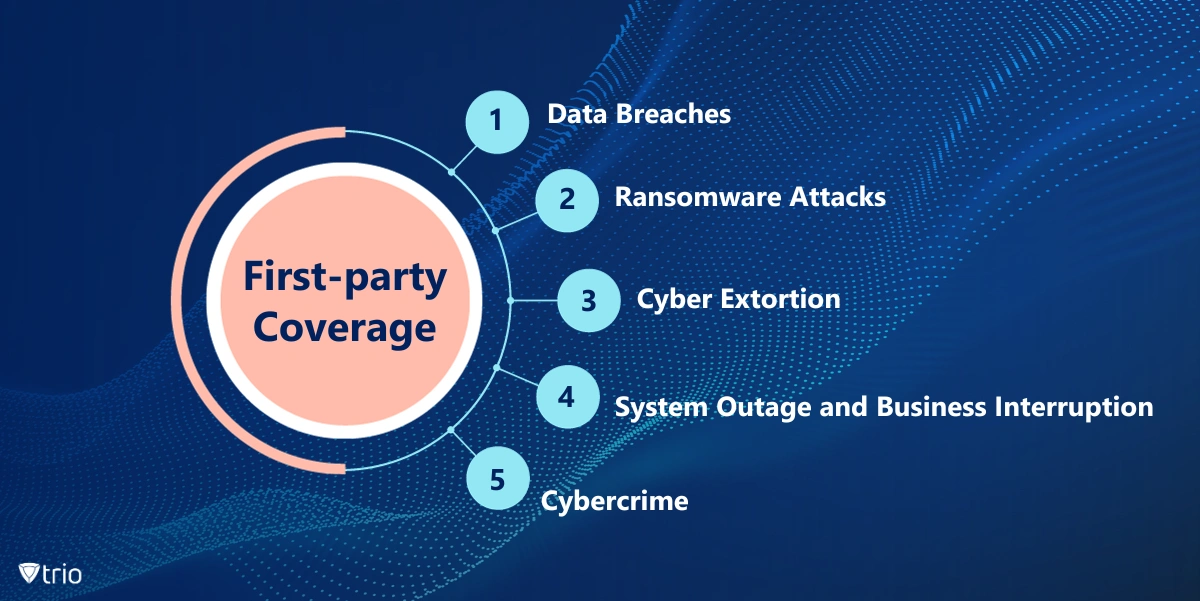
First-party Coverage
First-party coverage protects your own company from the costs of a data breach or cyberattack that happens on your own network or systems.
- Data Breaches: This covers costs associated with a data breach, including forensic investigation, notification to affected individuals, credit monitoring services, and public relations.
- Ransomware Attacks: Helps cover the ransomware attack payment, data restoration costs, and lost business income during the outage.
- Cyber Extortion: Provides financial assistance if hackers threaten to release sensitive data or disrupt operations unless demands are met.
- System Outage and Business Interruption: Reimburses lost revenue and operating expenses incurred while your systems are down due to a cyberattack.
- Cybercrime: This may cover legal fees, fines, and penalties resulting from cybercrime lawsuits.
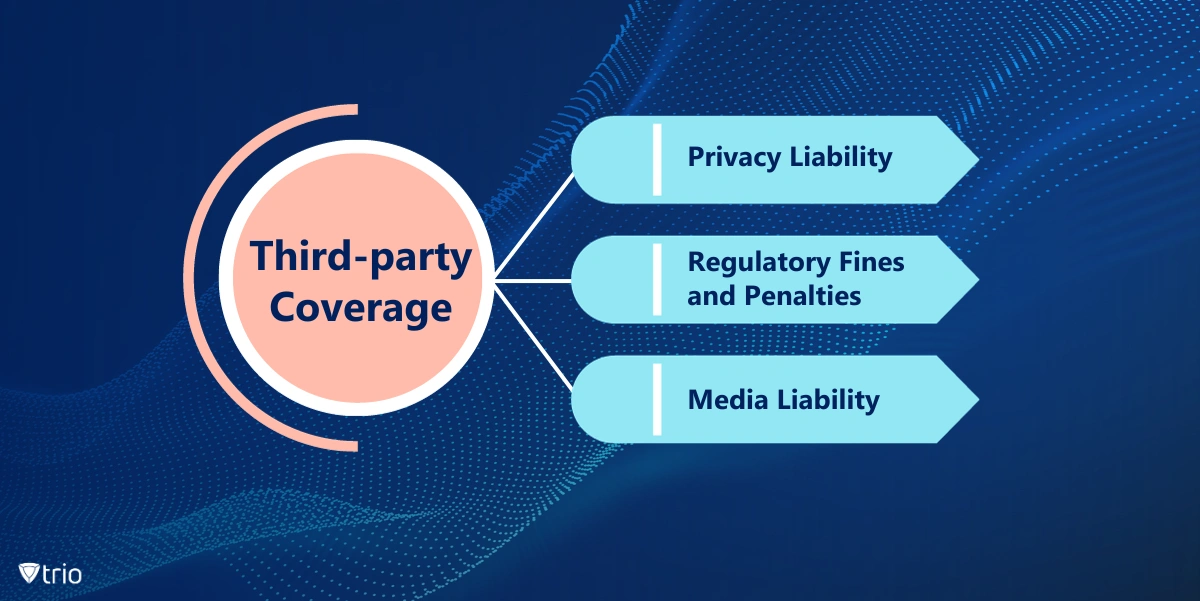
Third-party Coverage
Third-party coverage protects you from liability if a third party (such as a customer, business partner, or vendor) sues you because of a data breach or cyberattack.
- Privacy Liability: Protects against lawsuits alleging you failed to protect customer data.
- Regulatory Fines and Penalties: Covers fines resulting from regulatory non-compliance related to data breaches or cybersecurity failures.
- Media Liability: Provides for defense and damages associated with claims of defamation, copyright infringement, or other harm caused by your online activities.
Limits and Exclusions of Cybersecurity Insurance Policies
While cyber liability insurance offers protection against many cyber threats, it has its blind spots. It won’t shield you from consequences when you leave the door wide open, figuratively speaking. This means weak security practices, known vulnerabilities you haven’t patched, and employee missteps can leave you footing the bill yourself. Additionally, cybersecurity insurance will not cover costs incurred from an incident that happened before you purchased the policy. Insurance policies provide coverage for future events, not retroactive protection for past incidents.
Think of it this way: If a robber waltzes in because you forgot to lock the door, your homeowner’s insurance likely won’t cover the stolen goods. Similarly, cyber insurance won’t bail you out if basic security hygiene is lacking or human error hands the keys to the bad guys.
Implementing Cybersecurity Insurance
Proactive implementation of cybersecurity insurance necessitates the establishment of robust protocols. Conducting regular risk assessments, implementing stringent security controls, formulating a comprehensive cybersecurity insurance program, and integrating MDM systems are among the cybersecurity insurance requirements for successful implementation. These protocols collectively contribute to data loss prevention and fortifying the organization’s resilience against cyber threats.
As mentioned earlier, a good MDM solution assumes a pivotal role in the seamless implementation of cybersecurity insurance. By facilitating the management and security of mobile devices, these solutions substantially reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches, fortifying the organization’s overall cybersecurity posture.
To sustain the efficacy of cybersecurity measures, including MDM solutions, a commitment to regular updates and patches is indispensable. The ever-evolving nature of cyber threats mandates constant vigilance, and keeping all devices and security solutions up to date is paramount to mitigate vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals.

Employee Education
In the intricate tapestry of cybersecurity, the human element remains both the first line of defense and a potential vulnerability. Employee education emerges as a dynamic force, shaping the contours of an organization’s resilience against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. Beyond being a compliance checkbox, it is an ongoing commitment to cultivating a cybersecurity-conscious culture within the workforce.
Understanding the profound impact that well-informed employees can have on an organization’s security posture is paramount. Employee education extends far beyond mere technical training of the cybersecurity insurance industry; it encompasses cultivating a heightened awareness of cyber threats, fostering a sense of responsibility, and instilling a proactive mindset to identify and mitigate potential risks.
Moreover, an educated workforce contributes to incident response readiness. In the unfortunate event of a cyber incident, well-informed employees can act swiftly, following established protocols to contain and report the threat. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of the incident, expedites disaster recovery, and ensures that the organization remains agile in the face of adversity.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity insurance emerges as an indispensable tool in the contemporary business environment, offering financial protection amidst the relentless onslaught of cyber threats. Through a judicious evaluation of top cybersecurity insurance companies, the establishment of robust protocols, and a steadfast commitment to employee education, organizations can fortify their cybersecurity posture and traverse the digital landscape with unwavering confidence. Moreover, the integration of MDM solutions enhances the overall efficacy of cybersecurity measures, particularly in managing the risks associated with mobile devices.
As IT administrators, the imperative is clear – create a cybersecurity insurance checklist and invest judiciously in MDM solutions for optimal protection. Faced with a multitude of cybersecurity insurance companies, making an informed decision can be the difference between a crippling data breach and seamless business operations.
Trio is a powerful MDM solution that lets businesses manage, secure, and connect their mobile devices. It simplifies device deployment, automates workflows, streamlines employee management, and handles software efficiently. More importantly, Trio’s security features like data encryption, strong authentication, and real-time monitoring can significantly enhance a company’s cybersecurity posture, making it more attractive to insurance providers and potentially leading to lower premiums and better coverage. Don’t miss out on efficient software handling and strong authentication. Get your free demo and see the difference Trio makes!
Know about news
in your inbox
Our newsletter is the perfect way to stay informed about the latest updates,
features, and news related to our mobile device management software.
Subscribe today to stay in the know and get the most out of your mobile
devices with our MDM solution app.
Recent Posts

Erase the Risk: Protect with Zero Standing Privileges
Learn how zero standing privileges eliminate persistent access rights, enhance data security and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.

Understanding Access Control Types in Cybersecurity w/ Examples
Thorough understanding of access control types & the knowledge to make informed decisions about implementing security measures in your organization.

Cloud Data Protection: Safeguarding Information in the Cloud
Learn essential strategies for robust cloud data protection, exploring tools, best practices, and policies that safeguard sensitive information.





