A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is a malicious attempt to disrupt the normal functioning of a targeted server, service, or network by overwhelming it with a flood of internet traffic. In a DDoS attack, a large number of compromised devices, often referred to as "bots" or "zombies," are orchestrated to send traffic to the target simultaneously. These devices can include computers, servers, IoT devices, and other internet-connected devices that have been infected with malware and brought under the control of the attacker(s). The goal of a DDoS attack is to consume the target's resources, such as bandwidth, processing power, or memory, to the point where it becomes unavailable to legitimate users. This denial of service can disrupt business operations, cause financial losses, and damage the reputation of the targeted organization, which makes DDoS attack defense crucial. In addition to the immediate impact on availability and performance, DDoS attacks also pose significant IT risk management challenges, including potential data breaches, loss of customer trust, and regulatory compliance issues. In this blog, we’ll explain DDoS attacks in further detail and highlight DDoS attack prevention tools and how they can help your endpoints.

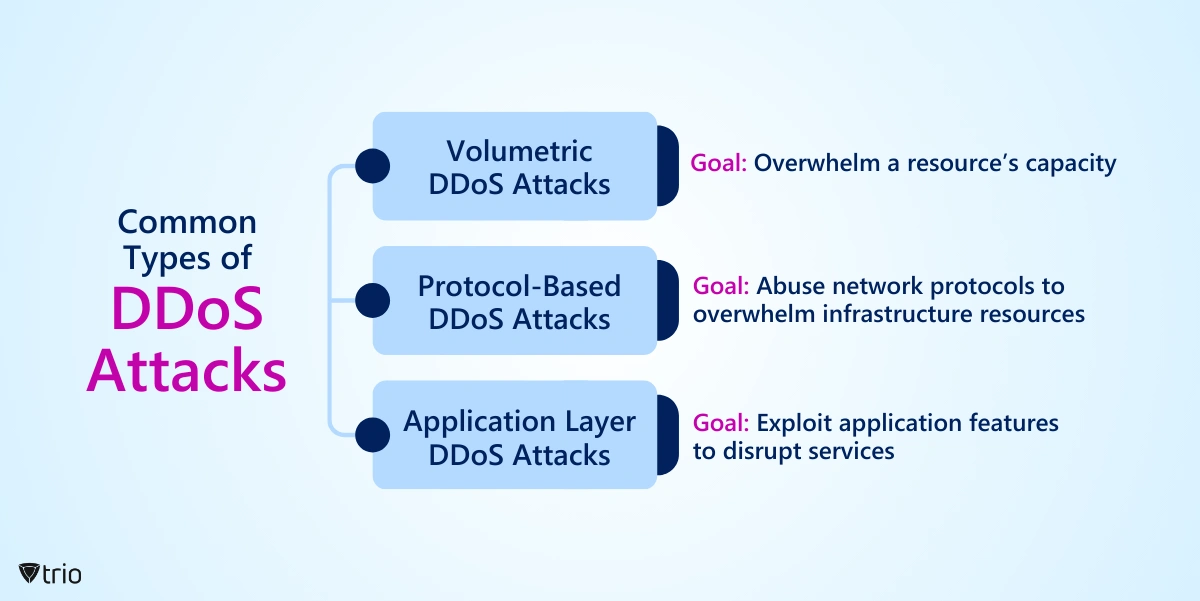
What Are the Common Types of DDoS Attacks?
There are different types of DDoS attacks that threat actors can use. The most common DDoS attacks are:
Volumetric DDoS Attacks
The goal of this attack is to overwhelm the target network or server with a high volume of traffic, consuming its available bandwidth and resources.
Methods that threat actors use:
- Utilize botnets to flood the target with massive amounts of junk data packets.
- Exploit vulnerabilities in protocols like UDP, ICMP, or TCP to amplify the attack traffic.
Protocol Attacks
The goal of this attack is to exploit weaknesses in network protocols to exhaust server resources or disrupt network communication.
Methods that threat actors use:
- SYN Flood: Send a large number of SYN requests, overwhelming the server's capacity to establish TCP connections.
- ICMP Flood: Flood the target with ICMP echo requests (ping), causing it to become unresponsive.
- UDP Flood: Flood the target with UDP packets, exploiting the connectionless nature of UDP to bypass connection setup overhead.
Application Layer Attacks
The goal of this attack is to target specific applications or services to disrupt their functionality or exhaust server resources.
Methods that threat actors use:
- HTTP Flood: Send a large volume of HTTP requests to overwhelm web servers, causing them to become unresponsive.
- DNS Amplification: Exploit misconfigured DNS servers to amplify attack traffic, causing DNS responses to be sent to the victim.
- Slowloris: Establish multiple partial connections to a web server, keeping them open to exhaust server resources.
Each type of DDoS attack aims to achieve its goals by exploiting weaknesses in different layers of the network stack or targeting specific applications or services. Understanding these attack types is essential for implementing effective DDoS prevention strategies.
What is DDoS Attack Protection?
DDoS attack protection encompasses strategies and measures aimed at defending against and mitigating the impact of DDoS attacks. While related, DDoS attack prevention specifically emphasizes proactive steps to minimize the likelihood of DDoS attacks.
Mitigation techniques typically include deploying specialized DDoS mitigation appliances or services to analyze incoming traffic, and identifying and filtering out DDoS attack traffic while allowing legitimate traffic to pass through. Additionally, cloud-based DDoS protection services can be leveraged to detect and mitigate attacks in real time by diverting attack traffic away from the targeted infrastructure and absorbing it within the cloud provider's network. By implementing these mitigation strategies, organizations can enhance their resilience against DDoS attacks and minimize the risk of service disruption.
Can You Prevent DDoS Attacks?
While it's difficult to prevent DDoS attacks entirely, it’s possible to mitigate their impact and reduce the likelihood of successful attacks.
DDoS prevention methods encompass implementing strategies to defend against attacks, aiming to stop malicious traffic and ensure legitimate users can access resources. Key strategies include strengthening network infrastructure, deploying firewalls, routers, and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to filter out malicious traffic, employing traffic scrubbing services or dedicated DDoS mitigation appliances to analyze and filter out DDoS traffic, utilizing Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to distribute website content across multiple servers, implementing rate limiting and traffic shaping mechanisms, deploying anomaly detection systems, leveraging cloud-based DDoS protection services, distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers using load balancers, and developing incident response plans. These measures enhance resilience against DDoS attacks and minimize the risk of service disruption. Additionally, regularly updating and patching systems is crucial to addressing known vulnerabilities.
Why Is It Important to Prevent DDoS Attacks?
Preventing DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks is crucial because these attacks can have detrimental effects on businesses, organizations, and even critical infrastructure. DDoS attacks can disrupt online services, rendering websites, and applications, or making entire networks inaccessible to legitimate users. This downtime can result in financial losses, damage to reputation, and loss of customer trust. Moreover, DDoS attacks can also be used as a smokescreen to conceal more sinister cyber threats, such as data breaches or malware infections, further exacerbating the potential damage. By implementing robust DDoS prevention measures, organizations can safeguard their online presence, maintain business continuity, and protect sensitive data and assets from exploitation by malicious actors.
What Is the Best Solution for DDoS Attack?
There is no single "best" solution for DDoS attacks, as effective mitigation often requires a combination of strategies and technologies tailored to the specific needs and infrastructure of an organization. However, by combining the preventive methods above, businesses can mitigate DDoS attacks.
![screen with firewall notification]](https://www.trio.so/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/ddos-attack-prevention-FAQ.webp)
Conclusion
Get Ahead of the Curve
Every organization today needs a solution to automate time-consuming tasks and strengthen security.
Without the right tools, manual processes drain resources and leave gaps in protection. Trio MDM is designed to solve this problem, automating key tasks, boosting security, and ensuring compliance with ease.
Don't let inefficiencies hold you back. Learn how Trio MDM can revolutionize your IT operations or request a free trial today!





