The landscape of cybersecurity is ever-evolving, marked by an increasing number of high-profile data breaches that have left organizations grappling with the consequences. One such notable example is Yahoo’s data breach spanning from 2013 to 2016, exposing over 3 billion user accounts—a stark reminder of the colossal impact breaches can have on individuals and entities. In addition to cybersecurity, IT risk management plays a crucial role in mitigating the potential fallout from data breaches. Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan (CIRP) is another vital aspect to consider, outlining the steps and procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security incidents. Read this blog to get the nuances of company data breaches, the methods by which they occur, and the critical steps organizations must take to prevent, recover from, and develop a long-term strategy against such incidents.
What Are Data Breaches?
A data breach refers to the unauthorized access, acquisition, disclosure, or use of sensitive information by individuals, organizations, or entities. These incidents can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, leading to potential harm for individuals or entities whose information is affected. A company data breach is an incident that occurs in a company.
The consequences of a data breach can be severe and may include financial losses, damage to reputation, identity theft, and legal repercussions. Organizations often implement security measures such as encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits to protect against data breaches.
Data Breach vs. Data Leak
While the terms “data breach” and “data leak” are often used interchangeably, there is a subtle difference.
A data leak specifically refers to the unauthorized release of information from a system or database. It may involve the unintentional exposure of sensitive data, such as through human error, misconfigured databases, or insecure application programming interfaces (APIs). Opposed to data breaches, data leaks can happen without malicious intent, and the term is often used to describe situations where information is inadvertently made accessible to unauthorized parties. All in all, the emphasis is on the accidental or inadvertent nature of the information release.
How do Data Breaches Happen?
Data breaches can occur through various methods, with attackers constantly evolving techniques to exploit vulnerabilities. Common avenues for company data breaches include phishing attacks, such as email phishing and spear phishing, where deceptive messages trick individuals into revealing sensitive information. Malware infections involve the use of malicious software like viruses or ransomware to compromise systems and gain unauthorized access. Weak passwords and credential theft pose risks through brute force attacks and credential stuffing, where stolen credentials are reused to access accounts. Insider threats, both malicious and accidental, can compromise security, while unpatched software vulnerabilities, supply chain attacks, and physical theft or loss of devices containing sensitive data further contribute to the risk.
Additionally, insecure APIs, man-in-the-middle attacks, social engineering, and inadequate network security measures are potential vectors for breaches. To mitigate these risks, organizations are advised to implement a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy encompassing regular security assessments, employee training, strong access controls, encryption, and timely software updates. The importance of continuous monitoring and robust incident response planning is emphasized for prompt detection and response to potential breaches. Adopting these measures collectively strengthens an organization’s defense against evolving cyber threats.

How Do You Recover from a Data Breach?
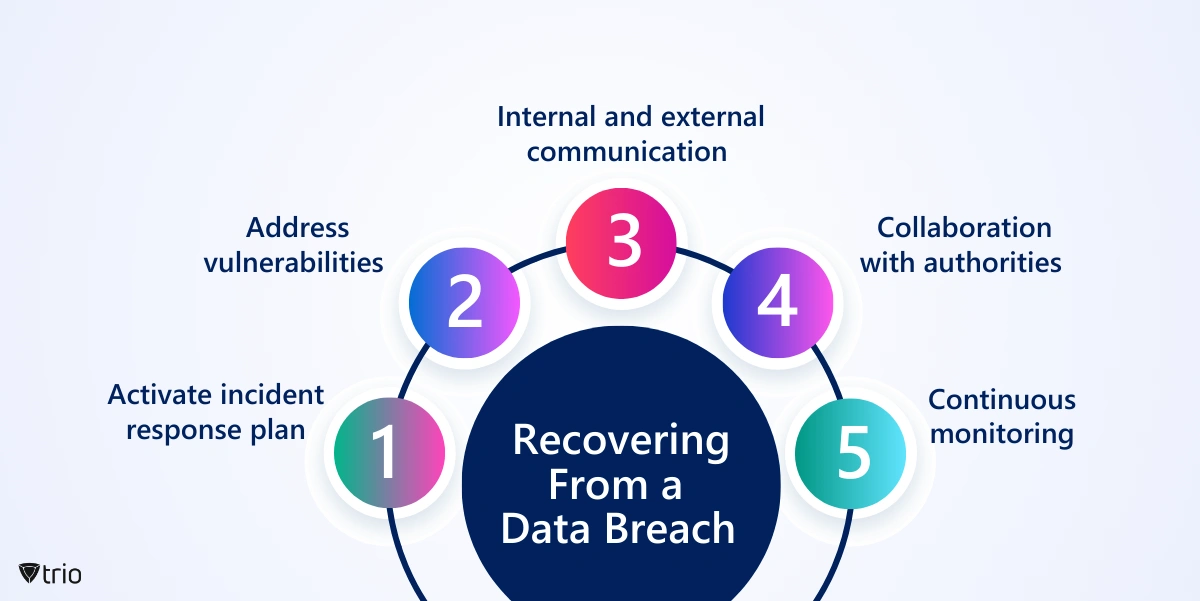
Recovering from a data breach demands a strategic and coordinated response. But what should a company do after a data breach? Companies facing such incidents should promptly activate their pre-established incident response plans, outlining responsibilities and communication procedures. Immediate containment efforts should isolate and address vulnerabilities, and law enforcement collaboration is essential for a thorough investigation. Internal and external communication is critical; stakeholders, customers, and regulatory bodies must be transparently informed. Support services, such as credit monitoring and identity theft protection, should be provided to affected individuals. Collaboration with authorities is vital for identifying and apprehending perpetrators. A forensic analysis helps understand the breach’s extent, enabling the strengthening of security measures, including system updates, additional controls, and enhanced employee training. Legal and regulatory compliance, trust rebuilding, post-incident reviews, continuous monitoring, and public relations strategies contribute to a comprehensive recovery approach. The multifaceted process requires decisive action to minimize the breach’s impact and rebuild trust with stakeholders.
Conclusion
As organizations navigate the delicate balance between employee flexibility and data breach prevention, it is imperative to comprehend the intricacies of these incidents. Data breaches, with their potential for severe repercussions, demand a multifaceted approach. From understanding the subtle differences between data breaches and leaks to exploring the myriad ways breaches can occur, the necessity for a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy becomes evident.
Moreover, integrating a Mobile Device Management (MDM) solution play a pivotal role in this strategy. MDM solutions empower organizations to manage and secure mobile devices, ensuring that sensitive corporate data is protected even in an era of heightened employee flexibility. By enforcing policies, monitoring device activities, and implementing remote data wipe capabilities, MDM solutions provide an added layer of defense against potential breaches. Recovering from a breach requires swift, strategic responses, but the ultimate goal is prevention. By adopting proactive measures, including the implementation of MDM solutions, organizations can fortify their defenses, foster a resilient cybersecurity culture, and develop a long-term strategy that adapts to the evolving threat landscape. In this era of persistent cyber threats, the commitment to safeguarding sensitive information, bolstered by MDM solutions, is not just a priority—it is an ongoing imperative.
Get Ahead of the Curve
Every organization today needs a solution to automate time-consuming tasks and strengthen security.
Without the right tools, manual processes drain resources and leave gaps in protection. Trio MDM is designed to solve this problem, automating key tasks, boosting security, and ensuring compliance with ease.
Don't let inefficiencies hold you back. Learn how Trio MDM can revolutionize your IT operations or request a free trial today!