In today’s dynamic IT landscape, where systems and applications are constantly evolving, maintaining a desired state across diverse environments is a paramount challenge. This is where configuration management comes into play, empowering organizations to streamline operations, enhance security, and drive continuous compliance. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of configuration management, exploring its strategies, tools, software, systems, and services tailored for network and cloud infrastructure.
Demystifying Configuration Management
Configuration management is a disciplined approach to systematically tracking, controlling, and maintaining the integrity of IT assets throughout their lifecycle. Its primary objective is to ensure that hardware, software, and network components operate in a consistent, predictable, and desired configuration state, minimizing the risks of configuration drift, security vulnerabilities, and performance degradation.
At its core, configuration management involves identifying, documenting, and managing the functional and physical attributes of configuration items (CIs) – any component, service, or asset that contributes to the delivery of IT services. This process encompasses a wide range of activities, from establishing baselines and enforcing standardized configurations to monitoring changes, assessing compliance, and implementing remediation measures when deviations occur.
The Compelling Case for Configuration Management
Effective configuration management offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond mere operational efficiency. By implementing robust configuration management practices, organizations can:
Enhance System Reliability and Availability: Consistent configurations minimize the likelihood of errors, downtime, and performance issues, ensuring that systems operate as intended and meet service level agreements (SLAs).
Strengthen Security Posture: By establishing and enforcing standardized security configurations, organizations can mitigate risks, prevent unauthorized changes, and maintain compliance with industry regulations and internal policies.
Facilitate Change Management: Configuration management enables organizations to track and control changes to IT assets, reducing the risk of unintended consequences and ensuring that changes are properly documented, tested, and approved.
Improve Operational Efficiency: Automated configuration management processes streamline tasks such as software deployment, patch management, and system provisioning, reducing manual effort and minimizing human errors.
Enable Rapid Incident Response: With comprehensive documentation and visibility into system configurations, IT teams can quickly identify root causes and implement targeted remediation measures, minimizing the impact of incidents and reducing recovery time.
The Configuration Management Lifecycle
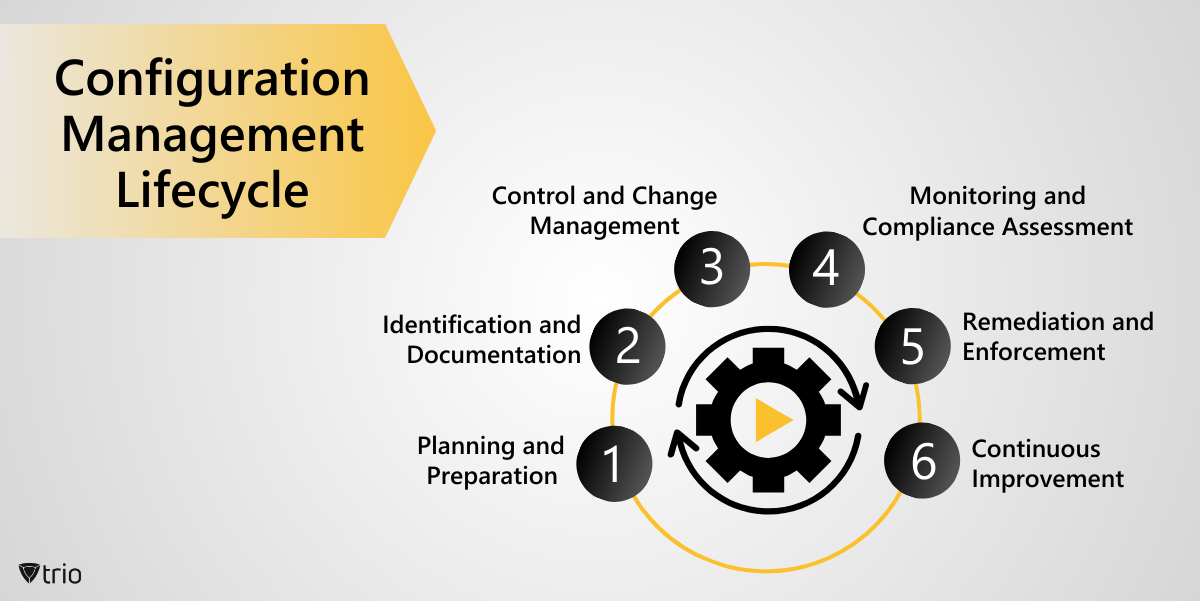
Effective configuration management is a continuous process that spans the entire lifecycle of IT assets. The following stages outline the typical configuration management lifecycle:
-
Planning and Preparation
In this initial stage, organizations define their configuration management objectives, scope, and policies. This includes identifying the configuration items to be managed, establishing roles and responsibilities, and defining the desired state for each asset.
-
Identification and Documentation
Once the scope is defined, IT teams document the current state of the environment, capturing detailed information about hardware, software, network configurations, and their interdependencies. This baseline serves as a reference point for future changes and compliance assessments.
-
Control and Change Management
Robust change management processes are implemented to ensure that all modifications to IT assets are properly reviewed, approved, and documented. This stage involves defining change control procedures, establishing approval workflows, and implementing version control mechanisms.
-
Monitoring and Compliance Assessment
Continuous monitoring is essential to detect deviations from the desired state and assess compliance with established policies and regulations. This stage involves deploying monitoring tools, defining metrics and thresholds, and generating reports for analysis and remediation.
-
Remediation and Enforcement
When deviations or non-compliance issues are identified, appropriate remediation measures are taken to bring the affected assets back into compliance. This may involve automated remediation scripts, manual interventions, or a combination of both, depending on the complexity and impact of the issue.
-
Continuous Improvement
The configuration management process is iterative, and organizations should continuously evaluate and refine their practices based on lessons learned, changing business requirements, and emerging technologies. Regular reviews and audits help identify areas for improvement and ensure that the configuration management strategy remains aligned with organizational goals.
Configuration Management Tools and Software
To effectively implement and manage configuration management processes, organizations leverage a variety of tools and software solutions. These tools automate various tasks, provide centralized control, and enable organizations to scale their configuration management efforts across complex environments. Some popular configuration management tools include:
Ansible: An open-source automation platform that simplifies IT automation, including configuration management, application deployment, and orchestration tasks.
Puppet: A configuration management tool that uses a declarative language to define and enforce desired system states, enabling automated provisioning, patching, and compliance enforcement.
Chef: A configuration management and automation platform that treats infrastructure as code, allowing users to define and manage system configurations through reusable “recipes.”
SaltStack: A Python-based configuration management and remote execution engine designed for rapid data collection and scalable management of large-scale environments.
Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager: A comprehensive management solution for deploying operating systems, applications, software updates, and managing device settings across an enterprise.
Network Configuration Management
In the realm of network infrastructure, configuration management plays a critical role in ensuring consistent and secure network operations. Network configuration management involves managing and maintaining the configurations of network devices, such as routers, switches, firewalls, and load balancers, across the enterprise.
- Effective network configuration management enables organizations to:
- Establish and enforce standardized network configurations, reducing the risk of misconfigurations and security vulnerabilities.
- Automate network device provisioning, software updates, and configuration changes, minimizing manual effort and errors.
- Monitor and detect unauthorized changes or deviations from approved configurations, enabling proactive remediation.
- Maintain an audit trail of all network configuration changes, facilitating compliance reporting and troubleshooting.
- Streamline network change management processes, ensuring that changes are properly reviewed, tested, and approved before implementation.
Popular network configuration management tools include SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager, Cisco Prime Infrastructure, and Infoblox NetMRI, among others.

Cloud Configuration Management
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud computing, managing configurations across hybrid and multi-cloud environments has become a critical challenge. Cloud configuration management involves maintaining consistent configurations for cloud resources, such as virtual machines, storage, networks, and applications, across public, private, and hybrid cloud environments.
- Effective cloud configuration management enables organizations to:
- Ensure consistent configurations across multiple cloud platforms, reducing the risk of misconfigurations and security vulnerabilities.
- Automate the provisioning and decommissioning of cloud resources, minimizing manual effort and errors.
- Maintain an audit trail of all cloud configuration changes, facilitating compliance reporting and troubleshooting.
- Streamline cloud resource lifecycle management, ensuring that resources are properly provisioned, configured, and decommissioned when no longer needed.
- Integrate with cloud provider tools and APIs for seamless management of cloud resources.
Popular cloud configuration management tools include Ansible, Terraform, CloudFormation, and Azure Resource Manager, among others.
Choosing the Right Configuration Management System
Selecting the appropriate configuration management system is crucial for ensuring successful implementation and maximizing the benefits of configuration management. When evaluating potential solutions, organizations should consider the following factors:
Scalability: The ability of the system to handle the organization’s current and future configuration management needs, including the number of devices, complexity of the environment, and rate of change.
Compatibility: Compatibility with the organization’s existing IT infrastructure, including operating systems, network devices, cloud platforms, and other management tools.
Automation Capabilities: The level of automation support offered by the system, including automated discovery, configuration enforcement, and remediation.
Reporting and Auditing: The system’s ability to generate comprehensive reports and maintain audit trails for compliance and troubleshooting purposes.
Integration: The ability to integrate with other IT management systems, such as change management, incident management, and service desk solutions.
Vendor Support and Community: The level of vendor support, documentation, and community resources available for the system.
Cost: The total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance and support costs.
The Role of Mobile Device Management (MDM) in Configuration Management
In today’s mobile-centric world, where employees access corporate resources from various devices and locations, managing and securing these devices has become a critical aspect of configuration management. Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions play a crucial role in ensuring that mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, are properly configured, secured, and compliant with organizational policies.
MDM solutions enable organizations to:
- Enforce security policies and configurations on mobile devices, including password requirements, device encryption, and remote wipe capabilities.
- Manage and distribute mobile applications, updates, and configurations to authorized devices.
- Monitor and track mobile device inventory, usage, and compliance status.
- Integrate with existing configuration management systems and IT management tools for a unified approach to device management.
One such MDM solution is Trio MDM, which offers a comprehensive suite of features for managing and securing mobile devices across various platforms, including iOS, Android, and Windows. Trio MDM provides IT administrators with centralized control over device configurations, app management, and security policies, ensuring that mobile devices remain compliant and secure, even in remote or hybrid work environments.
To witness firsthand the positive impact such a system can have on your operation, we invite you to try out Trio’s free demo and see how you can make a difference in IT automation at your organization.
Implementing Configuration Management: A Roadmap
Implementing an effective configuration management strategy requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing maintenance. Here is a high-level roadmap to guide organizations through the implementation process:
- Define Objectives and Scope: Clearly define the objectives and scope of your configuration management initiative, including the IT assets, environments, and processes to be covered.
- Assess Current State: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of your current IT infrastructure, documenting existing configurations, processes, and tools.
- Select Configuration Management Tools: Evaluate and select the appropriate configuration management tools and software based on your organization’s requirements, existing infrastructure, and future growth plans.
- Develop a Configuration Management Plan: Create a detailed configuration management plan that outlines policies, procedures, roles and responsibilities, and the desired state for each configuration item.
- Establish Baselines: Document the baseline configurations for all IT assets, including hardware, software, network devices, and cloud resources.
- Implement Change Management Processes: Establish robust change management processes to ensure that all configuration changes are properly reviewed, approved, and documented.
- Train and Educate: Provide comprehensive training and education to IT staff, stakeholders, and end-users on the configuration management processes, tools, and best practices.
- Deploy and Automate: Deploy the selected configuration management tools and automate configuration management processes to streamline operations and ensure consistency.
- Monitor and Assess: Continuously monitor and assess the effectiveness of your configuration management strategy, identifying areas for improvement and addressing any issues or deviations.
- Continuously Improve: Regularly review and refine your configuration management processes, incorporating lessons learned, best practices, and emerging technologies to ensure ongoing effectiveness and alignment with organizational goals.
See Trio in Action: Get Your Free Trial Now!
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of IT, where complexity and change are constants, configuration management emerges as a critical discipline for organizations seeking to maintain control, consistency, and compliance across their networks and cloud environments. By implementing effective configuration management strategies, organizations can streamline operations, enhance security, and drive continuous compliance, ultimately ensuring that their IT assets operate in a desired state, supporting business objectives and enabling digital transformation.
With the right configuration management service, your organization can navigate the intricacies of config management, automating processes, enforcing standardized configurations, and maintaining an audit trail of changes. By embracing configuration management best practices and leveraging the power of solutions like Trio MDM, organizations can stay ahead of the curve, ensuring that their IT infrastructure remains reliable, secure, and aligned with business goals.




