LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) serves as a cornerstone in modern IT infrastructures, offering centralized authentication, directory services, and efficient information retrieval capabilities over networked environments. Understanding how LDAP works and its benefits is crucial for organizations seeking to streamline user management, enhance security, and improve access control across their IT systems. Read on to learn more about how LDAP works and what its benefits are for your organization.
What Is LDAP?
LDAP stands for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. It’s a protocol used for accessing and maintaining directory services over a network. LDAP is commonly used for centralized authentication, directory services, and information lookups.
LDAP directories are hierarchical databases that store information about users, groups, and other resources in a networked environment. This information can include user credentials, contact information, access permissions, and more. LDAP allows clients to search, retrieve, and modify this information from the directory server.

How Does LDAP Work?
LDAP works as a client-server protocol in a hierarchical manner. LDAP operates on a client-server model, where LDAP clients interact with LDAP servers to access directory information. The client sends requests to the server, which processes them and returns the results.
LDAP directories are organized in a hierarchical structure similar to a tree. At the top of the tree is the root directory, and beneath it are branches representing organizational units (OUs), which can contain further subunits or leaf nodes representing individual entities like users, groups, or resources.
LDAP communication occurs over TCP/IP using a well-defined protocol. Typically, LDAP uses port 389 for unsecured connections and port 636 for connections secured with SSL/TLS. The LDAP client initiates a connection to the LDAP server and performs a bind operation to authenticate itself. The bind operation includes providing credentials (such as a username and password) to the server for authentication.
Once authenticated, the client can send search requests to the LDAP server to retrieve directory information. Search requests specify search criteria such as attributes to match, search base (the starting point in the directory tree), and scope (whether to search only the base object, one level below, or the entire subtree).
The LDAP server processes the search request and returns matching entries from the directory. Entries are returned in a hierarchical format, with each entry containing attributes and their values. LDAP also supports operations to add, modify, or delete directory entries. Clients can send modify requests to the server to update directory information. These modifications are typically subject to access controls and permissions defined by the directory administrator.
Is LDAP Secure?
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) itself does not provide inherent security features such as encryption or authentication mechanisms. However, LDAP can be secured through additional measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of directory data and communications. Here are some common security measures used to enhance LDAP security:
- SSL/TLS Encryption: LDAP communication can be secured using SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or its successor TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols. This encrypts data transmitted between LDAP clients and servers, preventing eavesdropping and tampering by unauthorized parties.
- LDAPS (LDAP over SSL/TLS): LDAPS is a variant of LDAP that uses SSL/TLS encryption to secure LDAP communication. LDAPS encrypts data exchanged between LDAP clients and servers, providing an additional layer of security for directory access and authentication.
- Authentication Mechanisms: There are a variety of LDAP authentication mechanisms, including simple authentication (username and password), SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer), and Kerberos. Organizations can choose appropriate authentication methods based on their security requirements and infrastructure.
- Access Control: LDAP directories often implement access control mechanisms to restrict access to directory data based on user permissions and roles. Access control lists (ACLs) can be used to define granular access policies for directory objects, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive information. By integrating LDAP with software management systems, organizations can ensure that only authorized users can access specific software, enhancing security and compliance.
- Firewall and Network Security: Implementing firewalls and network security measures can protect LDAP servers from unauthorized access and network-based attacks. Restricting access to LDAP services to trusted IP addresses and networks can help prevent unauthorized access attempts.
- Directory Server Hardening: Properly configuring and hardening LDAP servers can enhance security by reducing the attack surface and mitigating common security vulnerabilities. This includes applying security patches regularly, disabling unnecessary services, and configuring strong authentication and encryption settings.

Benefits of LDAP
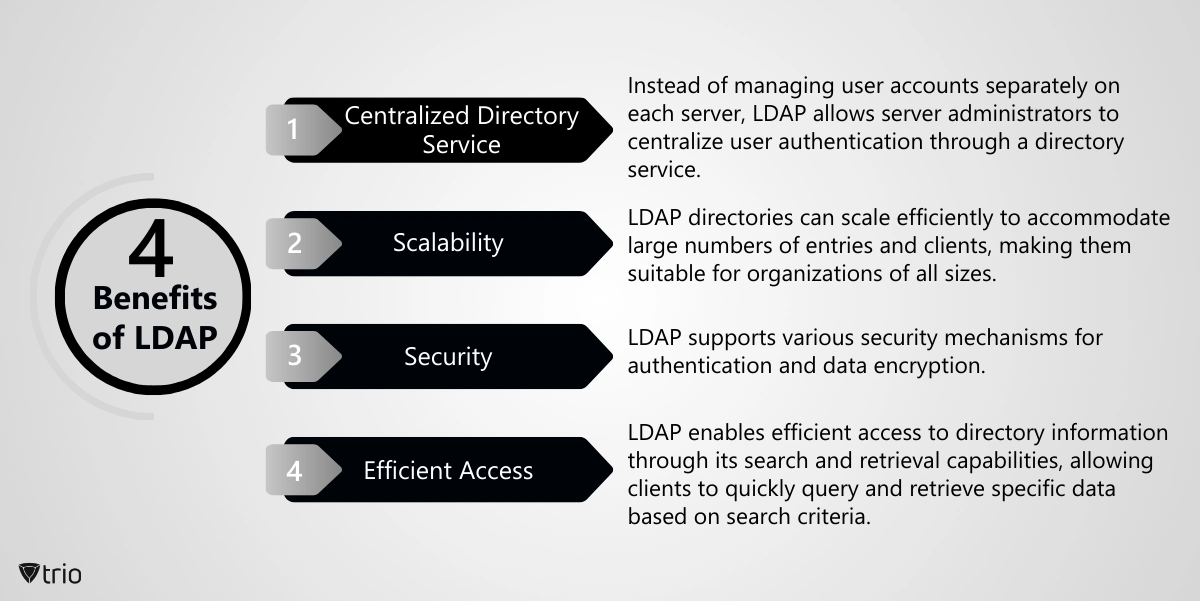
LDAP has many benefits for organizations. Here are the four most important ones.
- Centralized Directory Service: Instead of managing user accounts separately on each server, LDAP allows server administrators to centralize user authentication through a directory service. This simplifies user and server management. LDAP servers can be standalone applications or integrated into larger identity management systems such as Active Directory or OpenLDAP.
- Scalability: LDAP directories can scale efficiently to accommodate large numbers of entries and clients, making them suitable for organizations of all sizes. LDAP is commonly used in conjunction with other directory services and authentication systems. For example, Active Directory (AD) is a directory service developed by Microsoft that utilizes LDAP as its primary protocol for accessing and managing directory information. LDAP queries are commonly used to interact with Active Directory to perform tasks such as user authentication, accessing directory information, and managing objects like users, groups, and computers.
- Security: LDAP supports various security mechanisms for authentication and data encryption. Authentication can be done using simple authentication (username and password) or more secure methods like SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer). Additionally, LDAP can use SSL/TLS encryption to secure communication between the client and server.
- Efficient Access: LDAP enables efficient access to directory information through its search and retrieval capabilities, allowing clients to quickly query and retrieve specific data based on search criteria. LDAP servers often support replication, allowing directory data to be replicated across multiple servers for redundancy and scalability. This ensures high availability and fault tolerance in case of server failures.
What Organizations Use LDAP?
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) can be beneficial for various types of organizations, particularly those that require centralized management of directory information and authentication services. Here are some examples of organizations that can benefit from using LDAP:
-
Large Enterprises
Large enterprises with extensive user bases, multiple departments, and complex IT infrastructures can benefit from LDAP’s centralized directory services. LDAP helps streamline user management, access control, and authentication across the organization.
-
Government Agencies
Government agencies often need robust identity management solutions to manage user accounts, access permissions, and directory information securely. LDAP provides a standardized and scalable platform for centralized directory services in government environments.
-
Educational Institutions
Universities, colleges, and schools can use LDAP to manage student, faculty, and staff accounts, as well as access to resources such as library databases, email services, and learning management systems. LDAP’s scalability and flexibility make it suitable for educational environments with diverse user populations.
-
Healthcare Organizations
Healthcare organizations, including hospitals, clinics, and medical practices, require secure and efficient access to patient records, employee information, and other sensitive data. LDAP can help manage user identities, access controls, and compliance requirements in healthcare environments.
-
Corporate Networks
Businesses of all sizes can benefit from LDAP for centralized user authentication, access control, and directory services. LDAP integrates with various applications and services, making it a versatile solution for managing user accounts and access permissions in corporate networks.
-
Nonprofit Organizations
Nonprofit organizations with limited resources can benefit from LDAP’s cost-effectiveness and scalability. LDAP helps streamline user management processes, improve security, and ensure efficient access to resources for staff, volunteers, and stakeholders.
See Trio in Action: Get Your Free Trial Now!
Conclusion
In conclusion, organizations looking to optimize their IT infrastructure and enhance security can leverage LDAP to streamline user management processes and enforce consistent security policies across servers and mobile devices. Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions like Trio can integrate with LDAP for centralized user authentication and access control in mobile environments. Use this opportunity to try out Trio’s free demo and see how LDAP is smoothly integrated in the app.
From its hierarchical structure to the intricacies of authentication and directory services, LDAP offers organizations a robust framework for centralized management, efficient access, and enhanced security across networked environments.




