Two pivotal concepts, the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) and Information Technology Service Management (ITSM), have emerged as indispensable tools for streamlining organizations’ operations. While ITIL provides a framework of best practices, ITSM encompasses the overarching processes and methodologies for managing IT services. This article aims to put ITIL vs ITSM, demystifying the intricate relationship between ITIL and ITSM, shedding light on their distinctions, similarities, and the synergies that can propel your organization toward operational excellence.
Defining ITIL ITSM Meaning: The Backbone of IT Service Management
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a comprehensive set of guidelines and best practices that serve as a blueprint for delivering high-quality IT services. Developed in the 1980s by the British government, ITIL has evolved into a globally recognized standard, providing a structured approach to managing the entire life cycle of IT services.
ITIL’s primary objective is to align IT operations with business needs, fostering a seamless integration between technology and organizational goals. By adopting ITIL best practices, organizations can optimize their IT service delivery, enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
ITIL Service Strategy: A Holistic Approach
At the core of ITIL lies the ITIL Service Lifecycle, a cyclical model that encompasses five key stages:
Service Strategy: This stage focuses on aligning IT services with business objectives, ensuring that IT investments deliver tangible value to the organization.
Service Design: During this phase, organizations design and develop IT services that meet the identified business requirements, considering factors such as scalability, resilience, and cost-effectiveness.
Service Transition: This stage involves the seamless transition of new or modified IT services into the live production environment, minimizing disruptions and ensuring smooth service delivery.
Service Operation: This phase encompasses the day-to-day management of IT services, including incident management, problem management, and request fulfillment.
Continual Service Improvement: This ongoing process aims to identify opportunities for enhancing IT service quality, efficiency, and alignment with evolving business needs.
Exploring ITSM Support Model: The Overarching Methodology
Information Technology Service Management (ITSM) is a holistic approach that encompasses the processes, policies, and practices necessary for managing and delivering IT services effectively. ITSM extends beyond the technical aspects of IT, encompassing the entire service lifecycle, from strategy and design to implementation and ongoing support.
ITSM’s primary objective is to align IT services with business objectives, ensuring that IT investments contribute to organizational success. By adopting an ITSM approach, organizations can streamline their IT operations, improve service quality, enhance customer satisfaction, and maximize the return on their IT investments.
The Synergy: ITSM and ITIL Support Framework
While ITIL and ITSM are distinct concepts, they are intrinsically linked and complementary. ITIL serves as a comprehensive framework that provides best practices and guidelines for implementing effective ITSM processes. By leveraging ITIL’s principles and methodologies, organizations can establish a robust ITSM strategy that aligns with industry standards and proven best practices.
The relationship between ITIL and ITSM can be likened to a blueprint and a construction project. ITIL acts as the blueprint, providing a detailed set of instructions and guidelines for building a well-designed and functional structure. ITSM, on the other hand, represents the actual construction process, where the organization implements the necessary processes, tools, and resources to bring the blueprint to life.
Difference Between ITIL and ITSM Framework: Key Distinctions
While ITIL and ITSM are closely intertwined, it is crucial to understand their distinct characteristics and roles within the IT service management landscape:
Scope: ITIL is a comprehensive framework that provides best practices and guidelines for various aspects of IT service management, including service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement. In contrast, ITSM is a broader concept that encompasses the overall management of IT services, encompassing processes, tools, and organizational structures.
Focus: ITIL primarily focuses on the processes and activities involved in delivering and supporting IT services, while ITSM takes a more holistic approach, considering the strategic alignment of IT services with business objectives, customer satisfaction, and organizational culture.
Implementation: ITIL provides a structured set of guidelines and recommendations, but it does not prescribe a specific implementation methodology. ITSM, on the other hand, involves the actual implementation of processes, tools, and organizational structures to manage IT services effectively.
Flexibility: While ITIL offers a standardized framework, it allows for flexibility in adapting its principles to an organization’s unique needs and requirements. ITSM, being a broader concept, can incorporate various frameworks, methodologies, and tools, including but not limited to ITIL, to achieve its objectives.
Certification: ITIL offers a range of certification programs, such as ITIL Foundation, ITIL Practitioner, and ITIL Expert, which validate an individual’s knowledge and proficiency in applying ITIL best practices. ITSM, being a broader concept, does not have a standardized certification program, although some organizations may offer ITSM-specific training and certifications.
Real-World Applications: ITSM and ITIL Support Examples
To illustrate the practical applications of ITSM and ITIL, let’s explore a few real-world scenarios:
Service Desk Operations: A well-designed service desk is a crucial component of effective IT service management. By implementing ITIL best practices for incident management, problem management, and request fulfillment, organizations can streamline their service desk operations, improve response times, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Change Management: Effective change management is essential for minimizing service disruptions and ensuring smooth transitions when introducing new or modified IT services. ITIL’s guidelines for change management provide a structured approach to assessing, planning, and implementing changes, minimizing risks, and ensuring compliance with organizational policies and regulatory requirements.
Asset and Configuration Management: Maintaining an accurate inventory of IT assets and configurations is critical for effective service delivery and support. ITIL’s best practices for asset and configuration management enable organizations to establish a centralized repository of IT assets, track their life cycles, and ensure that configurations are properly documented and maintained.
Continual Service Improvement: Embracing the principle of continual service improvement is essential for staying ahead in the ever-changing IT landscape. By implementing ITIL’s guidelines for continual service improvement, organizations can establish processes for identifying areas for enhancement, implementing improvements, and measuring the impact of those changes on service quality and business outcomes.
ITSM and ITIL in the Era of Digital Transformation
As organizations embrace digital transformation and adopt emerging technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), the role of ITSM and ITIL becomes even more critical. These frameworks provide the necessary guidance and best practices to navigate the complexities of modern IT environments, ensuring that organizations can effectively manage and support their evolving IT landscapes.
Cloud Service Management: With the increasing adoption of cloud services, ITIL and ITSM provide valuable insights into managing cloud-based IT services, ensuring seamless integration with on-premises infrastructure, and optimizing resource utilization.
DevOps and Agile Methodologies: ITIL and ITSM can be seamlessly integrated with DevOps and Agile methodologies, enabling organizations to achieve faster time-to-market, continuous delivery, and improved collaboration between development and operations teams.
Automation and Artificial Intelligence: By leveraging ITIL best practices for process automation and incorporating AI technologies, organizations can streamline routine tasks, enhance decision-making processes, and improve overall service delivery efficiency.
Internet of Things (IoT) Management: As IoT devices proliferate across various industries, ITIL and ITSM offer guidance on managing and securing these connected devices, ensuring proper asset management, incident response, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
The Role of IT Service Management ITSM Software
While ITIL provides the framework and ITSM encompasses the processes, the successful implementation of an effective IT service management strategy often relies on leveraging specialized software solutions. ITSM software tools are designed to automate and streamline various aspects of IT service delivery, including incident management, problem management, change management, asset management, and knowledge management.
By integrating ITSM software into your IT operations, your organization can benefit from:
Increased Efficiency: Automated workflows and streamlined processes reduce manual effort, minimizing errors and improving overall productivity.
Improved Visibility and Control: Centralized dashboards and reporting capabilities provide real-time insights into IT service performance, enabling proactive monitoring and informed decision-making.
Enhanced Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Integrated knowledge management features and collaboration tools foster knowledge sharing among IT teams, ensuring consistent service delivery and facilitating continuous improvement.
Better Customer Experience: Self-service portals, automated notifications, and real-time status updates improve transparency and communication with end-users, enhancing customer satisfaction.
When selecting an ITSM software solution, it is crucial to evaluate its alignment with ITIL best practices, as well as its ability to integrate with existing IT infrastructure and support the organization’s specific requirements.
Implementing ITSM and ITIL: A Roadmap for Success
Implementing an effective ITSM strategy based on ITIL best practices is a journey that requires careful planning, execution, and continuous improvement. Here’s a high-level roadmap to guide organizations through this process:
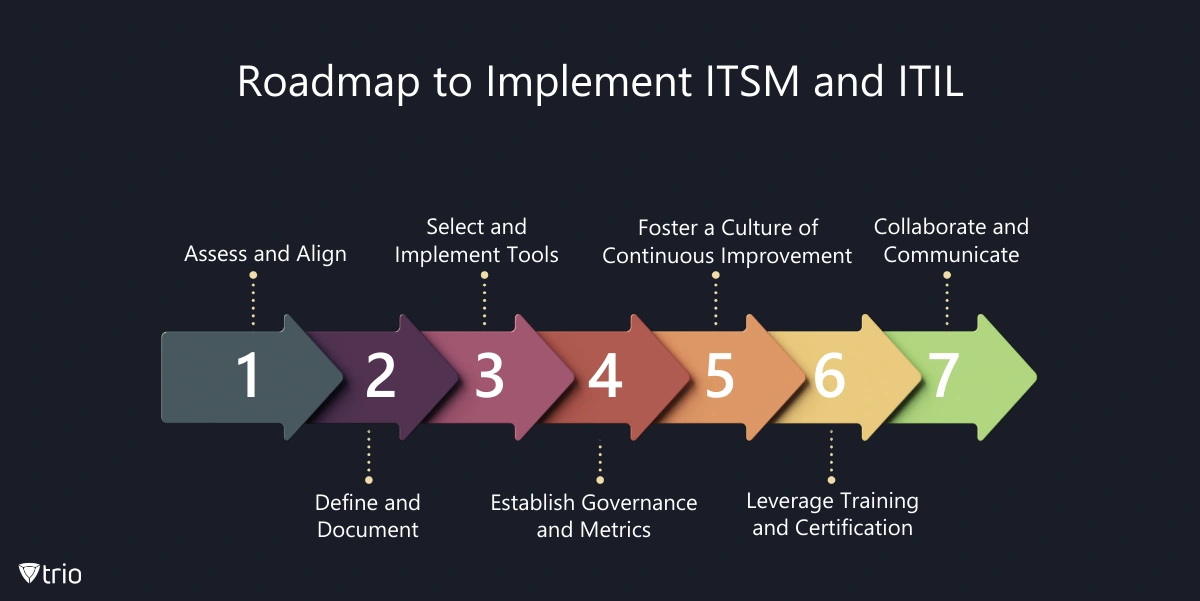
- Assess and Align: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of your organization’s current IT service management practices, identify gaps and areas for improvement, and align your ITSM strategy with business objectives and priorities.
- Define and Document: Clearly define and document your ITSM processes, roles, and responsibilities, leveraging ITIL best practices as a reference point. Ensure that these processes are tailored to your organization’s specific needs and aligned with industry standards.
- Select and Implement Tools: Evaluate and select ITSM software solutions that align with your processes and requirements. Implement these tools in a phased approach, ensuring proper training, documentation, and user adoption.
- Establish Governance and Metrics: Define a governance framework to oversee and monitor the implementation and ongoing operation of your ITSM processes. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure the success and effectiveness of your ITSM strategy.
- Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and refining your ITSM processes, leveraging feedback from stakeholders, and incorporating lessons learned from real-world experiences.
- Leverage Training and Certification: Invest in training and certification programs for your IT staff, ensuring they have the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively implement and maintain ITIL best practices and ITSM processes.
- Collaborate and Communicate: Foster collaboration and open communication among all stakeholders, including IT teams, business units, and end-users. Regularly communicate the benefits and progress of your ITSM implementation to maintain buy-in and support.
The Convergence of ITSM and Mobile Device Management (MDM)
In today’s mobile-driven workforce, the convergence of ITSM and mobile device management (MDM) has become increasingly crucial. MDM solutions play a vital role in managing and securing mobile devices within an organization, ensuring that these devices are properly configured, updated, and compliant with organizational policies.
By integrating MDM solutions with ITSM processes, your organization can streamline mobile device management, enhance security, and improve overall IT service delivery. Here are some key areas where ITSM and MDM converge:
Asset Management: MDM solutions enable organizations to maintain an accurate inventory of mobile devices, track their lifecycle, and ensure that they are properly managed and secured within the ITSM framework.
Configuration Management: MDM solutions work hand-in-hand with ITSM processes to ensure that mobile devices are properly configured and compliant with organizational policies, reducing the risk of security breaches and ensuring consistent service delivery.
Incident and Problem Management: By integrating MDM with ITSM incident and problem management processes, organizations can quickly identify and resolve issues related to mobile devices, minimizing downtime and improving end-user productivity.
Service Desk Integration: MDM solutions can be seamlessly integrated with ITSM service desk tools, enabling end-users to easily report issues, request support, and track the status of their mobile device-related requests.
Security and Compliance: MDM solutions play a crucial role in enforcing security policies, managing access controls, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, aligning with ITSM best practices for risk management and governance.
To effectively leverage the convergence of ITSM and MDM, you should consider implementing a comprehensive MDM solution that seamlessly integrates with your existing ITSM processes and tools. One such solution is Trio, a powerful MDM platform designed to simplify mobile device management and enhance IT service delivery.
Introducing Trio: A Comprehensive MDM Solution
Trio is a cutting-edge MDM solution that empowers organizations to effectively manage and secure their mobile device ecosystem, while seamlessly integrating with ITSM processes and tools. With Trio, you can:
Centralized Device Management: Gain complete visibility and control over all mobile devices within the organization, enabling remote configuration, software distribution, and policy enforcement.
Enhanced Security: Implement robust security measures, including device encryption, remote lock/wipe capabilities, and real-time threat detection, ensuring data protection and compliance.
Seamless Integration: Trio seamlessly integrates with popular ITSM tools and platforms, enabling streamlined mobile device management within existing IT service management workflows.
Simplified Deployment: Trio’s user-friendly interface and intuitive deployment process ensure a smooth and hassle-free implementation, minimizing disruptions to IT operations.
Scalability and Flexibility: Trio is designed to scale with your organization’s growing mobile device needs, offering flexible deployment options, including on-premises, cloud, or hybrid configurations.
To experience the power of Trio and unlock the full potential of ITSM and MDM convergence, we invite you to explore our free demo. Our experts will guide you through the features and capabilities of Trio, demonstrating how it can streamline your mobile device management processes and enhance overall IT service delivery.
ITIL vs ITSM: Final Words and Conclusion
In the realm of IT service management, ITIL vs ITSM are not mere buzzwords but powerful frameworks and methodologies that can propel your organization toward operational excellence. While ITIL provides the blueprint for best practices, ITSM encompasses the overarching processes and strategies for managing IT services effectively.
By embracing the synergy between ITIL and ITSM, your organization can establish a structured approach to IT service delivery, align its IT investments with business objectives, and drive continuous improvement. Additionally, the convergence of ITSM and MDM solutions, such as Trio, enables you to seamlessly manage and secure your mobile device ecosystem, further enhancing IT service delivery and ensuring a consistent and secure user experience.
The importance of ITIL and ITSM will only grow, providing organizations with the necessary tools and frameworks to navigate the complexities of modern IT environments. By investing in ITIL and ITSM best practices, you can future-proof your IT service management strategies, enabling yourself to adapt to emerging technologies, drive innovation, and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive business landscape.
Get Ahead of the Curve
Every organization today needs a solution to automate time-consuming tasks and strengthen security.
Without the right tools, manual processes drain resources and leave gaps in protection. Trio MDM is designed to solve this problem, automating key tasks, boosting security, and ensuring compliance with ease.
Don't let inefficiencies hold you back. Learn how Trio MDM can revolutionize your IT operations or request a free trial today!




