Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) is a comprehensive set of technologies and policies designed to secure and manage mobile devices, applications, and data within an organization. EMM solutions enable IT administrators to maintain control and oversight over the mobile ecosystem, ensuring that corporate data remains secure while allowing employees to use their mobile devices for work purposes. EMM is crucial for IT administrators in today's workplace. It's pivotal for ensuring security, compliance, and cost efficiency. EMM strengthens security with features like remote wipe and encryption, while streamlining app management and optimizing cost control. It automates IT tasks, enhances compliance, and supports remote troubleshooting, improving employee productivity and flexibility. EMM simplifies device management and enables the adoption of BYOD policies, making it an essential tool for modern enterprises.
Key Components of EMM
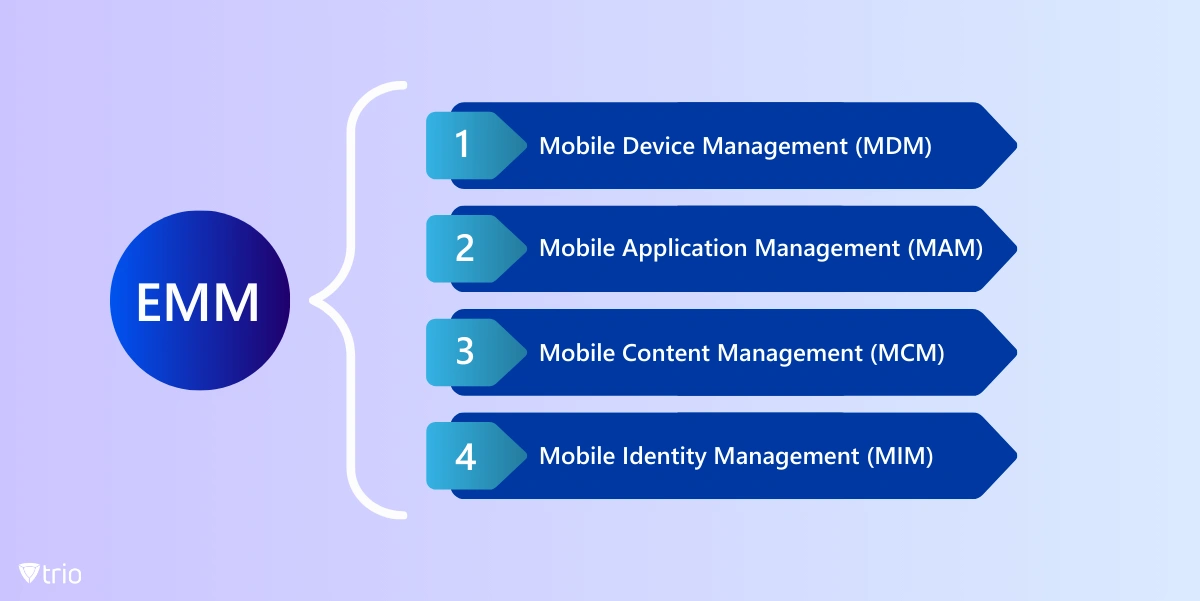
EMM is a comprehensive solution that is typically comprised of several interrelated and complementary modules or features, each focusing on specific aspects of mobile device and data management. These components work together to manage and secure an organization's mobile infrastructure. Each component is designed to address different aspects of enterprise mobility, such as device management, application management, content management, and identity management.
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
MDM is a core component of EMM responsible for controlling and securing mobile devices within an organization. It allows IT administrators to monitor and manage device settings, enforce security policies, and remotely configure or wipe devices if necessary. MDM ensures that devices comply with corporate security standards, such as encryption and password requirements, and provides features like device inventory, tracking, and remote lock and wipe capabilities to protect sensitive data.
Mobile Application Management (MAM)
MAM focuses on enterprise mobile management and security. It allows administrators to control the distribution of apps to devices, ensuring that employees have access to necessary business applications. MAM includes features like app whitelisting, blacklisting, and app containerization, which isolates business apps and data from personal content to enhance security. This component also provides insights into app usage and allows for the enforcement of app policies, such as updates and version control.
Mobile Content Management (MCM)
MCM is designed to protect and manage the content accessed and shared on mobile devices within the corporate environment. It facilitates secure access to corporate data repositories, ensuring that sensitive documents remain protected. MCM can enable features like content encryption, access controls, and the ability to remotely wipe corporate data from a device without affecting personal information. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access and modify enterprise content.
Mobile Identity Management (MIM)
MIM is essential for establishing and verifying the identities of users and devices that access an organization's mobile infrastructure. It encompasses authentication and access control mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication and single sign-on (SSO), to ensure that only authorized individuals gain access to enterprise resources. MIM also plays a crucial role in user provisioning and de-provisioning, helping to manage access to apps and data as employees join or leave the organization. It enhances security and simplifies user access, contributing to a seamless and secure mobile experience.
Assessing Readiness for EMM
Assessing your company's readiness for implementing EMM involves several steps. First, evaluate your current IT infrastructure by taking stock of the devices and operating systems in use, ensuring compatibility with the chosen EMM solution. Additionally, assess your network infrastructure, including Wi-Fi coverage and bandwidth, to ensure it can efficiently support increased mobile traffic. Evaluate your existing security protocols and practices to identify potential gaps or vulnerabilities that EMM can address.
Next, identify potential challenges and solutions. Anticipate security concerns such as data breaches, lost devices, or unauthorized access, and develop strategies for addressing these challenges using EMM's security features. Be prepared for potential user resistance by creating a communication plan that educates employees about the benefits and safeguards of EMM. Consider how EMM will integrate with your existing systems, ensuring it seamlessly works with email servers, directory services, and other enterprise applications.
Lastly, set up policies and guidelines. Develop clear EMM policies outlining rules, expectations, and security requirements for mobile device usage within your organization. Address factors like password policies, data encryption, app usage, and remote device management. Create user guidelines and training materials to educate employees about the EMM system and provide training and support for effective use. Ensure your EMM policies align with relevant industry and regulatory compliance requirements. This comprehensive approach to EMM readiness will not only prepare your organization for a smooth transition but also help you make informed decisions when selecting the right EMM solution for your specific needs.

Designing an EMM Strategy
Designing a comprehensive EMM strategy is a crucial step towards effectively managing your organization's mobile ecosystem. To create a robust strategy, follow these steps:
Define Scope and Goals: Identify your organization's objectives, such as enhancing security, boosting productivity, or reducing costs. Specify the scope of EMM, covering devices and platforms, and set measurable goals.
Determine Roles and Responsibilities: Define the roles of IT administrators and communicate user responsibilities, ensuring clarity and accountability.
Establish Communication Channels and Protocols: Set up effective communication channels for informing employees and creating support structures. Implement feedback mechanisms for continuous improvement.
Set Up Security Measures: Implement robust security measures for devices and data access, including encryption, access controls, and monitoring.
A well-structured EMM strategy aligns with organizational objectives, fosters clear communication, and prioritizes robust security to effectively manage the mobile environment. Regular assessment ensures continued alignment with evolving business needs and technology.
Implementing EMM
To successfully implement EMM in a company, follow these steps:
Provide Training and Support
Begin by offering comprehensive training for both IT administrators and employees. Ensure IT administrators understand the EMM system and that employees are educated on its use and related policies. Offer ongoing support to address questions and concerns.
Deploy EMM Solutions
Deploy your chosen EMM solutions to manage mobile devices and data access. This entails enrolling devices, enforcing EMM policies, distributing apps, and implementing data security measures. Continuously monitor device and data usage and manage devices remotely as needed.
Test and Refine
After the initial deployment, conduct thorough testing to identify issues and areas for improvement. Gather feedback on user experience, evaluate security measures, and assess system performance. Based on the results, refine the EMM strategy, adjust policies, enhance user training, and address any technical issues that arise.

Monitoring and Improving EMM
To effectively monitor and improve their EMM strategy, companies should adopt a proactive approach.
Collecting Feedback: Regularly gather feedback from IT administrators and employees to identify issues, concerns, and areas for improvement. This feedback is crucial for making informed adjustments and ensuring that the EMM system meets user expectations.
Analyzing Performance Metrics: Consistently analyze performance metrics covering device security, app performance, user satisfaction, and data access. This data provides valuable insights into the EMM system's effectiveness and allows companies to make necessary adjustments as needed.
Staying Up to Date: Stay current with industry trends and best practices in the EMM landscape. Attend conferences, webinars, and engage with industry peers to remain informed about evolving technologies and security threats. This knowledge enables companies to adapt their EMM strategy to stay competitive and secure.
Conclusion
In this blog we answered the question “What is EMM?” In conclusion, Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) is a multifaceted strategy designed to secure and enhance mobile device usage within organizations. Its key components, such as mobile device management (MDM), mobile application management (MAM), mobile content management (MCM), and mobile identity management (MIM), work together to provide comprehensive mobile management solutions. To effectively implement EMM, companies can choose an MDM solution like Trio to facilitate the process, allowing them to easily incorporate EMM services into their company. A well-executed EMM strategy, with the support of solutions like Trio, aligns with organizational objectives, fosters clear communication, and prioritizes security, allowing businesses to effectively navigate the dynamic mobile landscape.
Get Ahead of the Curve
Every organization today needs a solution to automate time-consuming tasks and strengthen security.
Without the right tools, manual processes drain resources and leave gaps in protection. Trio MDM is designed to solve this problem, automating key tasks, boosting security, and ensuring compliance with ease.
Don't let inefficiencies hold you back. Learn how Trio MDM can revolutionize your IT operations or request a free trial today!





