Endpoint security, also known as endpoint protection, involves safeguarding endpoints against malicious activities as part of cybersecurity measures. Now let’s take a step back, what’s considered an endpoint? Endpoints refer to devices that link to and share data with a computer network, some examples include mobile devices, computers, and servers. Organizations need their endpoints to be secured to prevent and detect malware and cyber-attacks. In this blog we’re going to cover everything, so you can answer the question “what is endpoint security?” with confidence!
Endpoint Security Components
Endpoint security typically comprises several components, each serving a specific purpose in defending endpoints against cyber threats. Some common components include:
- Antivirus/Anti-malware: Software designed to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software, including viruses, worms, Trojans, and spyware.
- Firewall: A network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It helps block unauthorized access and potential threats from reaching endpoints.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS): Monitors network traffic for suspicious activity or policy violations, alerts administrators, and can take action to prevent security incidents.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Advanced security solutions that continuously monitor and analyze endpoint activity to detect and respond to suspicious behavior or security incidents in real-time.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Technology that helps prevent unauthorized access, use, or transmission of sensitive data to safeguard against data breaches and maintain compliance with data protection regulations.
- Device Control: Allows organizations to define and enforce policies governing the use of removable devices, such as USB drives, to prevent data leakage and the introduction of malware.
- Patch Management: Ensures that endpoints are kept up to date with the latest security patches and updates to address vulnerabilities and minimize the risk of exploitation by attackers.
- Encryption: Protects data stored on endpoints or transmitted over networks by converting it into unreadable code that can only be accessed with the appropriate decryption key.
- Authentication and Access Control: Ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive resources and data on endpoints, typically through passwords, biometrics, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls.
- Endpoint Security Management: Centralized management consoles or platforms that enable administrators to deploy, configure, monitor, and maintain endpoint security solutions across the organization’s network.
These components work together to provide comprehensive protection for endpoints, helping organizations mitigate cybersecurity risks and safeguard critical assets and data.

Endpoint Security Benefits
Endpoint security, whether it be with endpoint detection and response (EDR) or an endpoint protection platform (EPP), offers a variety of benefits that can significantly improve an organization’s overall cybersecurity posture. Here are some of the key advantages:
Reduced Risk of Malware Infections: Endpoint security solutions like EPP and EDR protect devices from malware, ransomware, viruses, and other malicious software. This can prevent data breaches, financial losses, and disruptions to operations.
Enhanced Threat Detection and Response: An EDR solution goes beyond basic antivirus by continuously monitoring devices for suspicious activity. This allows for faster detection and response to advanced threats that might bypass traditional preventative measures.
Improved Data Security: Endpoint security can help safeguard sensitive data stored on devices through features like data encryption and data loss prevention (DLP). This minimizes the risk of data breaches even if a device is compromised.
Centralized Management and Visibility: EPP solutions offer a central console to manage security policies and configurations across all endpoints. This simplifies security administration and provides better visibility into the overall security posture of the organization.
Reduced Downtime: By preventing malware infections and other security incidents, endpoint security can help minimize device downtime and ensure business continuity.
Compliance with Regulations: Many industries have regulations that require organizations to protect sensitive data. Endpoint security solutions can help businesses meet these compliance requirements.
Improved User Productivity: When employees feel confident that their devices and data are secure, they can focus on their work without worrying about cyber threats.
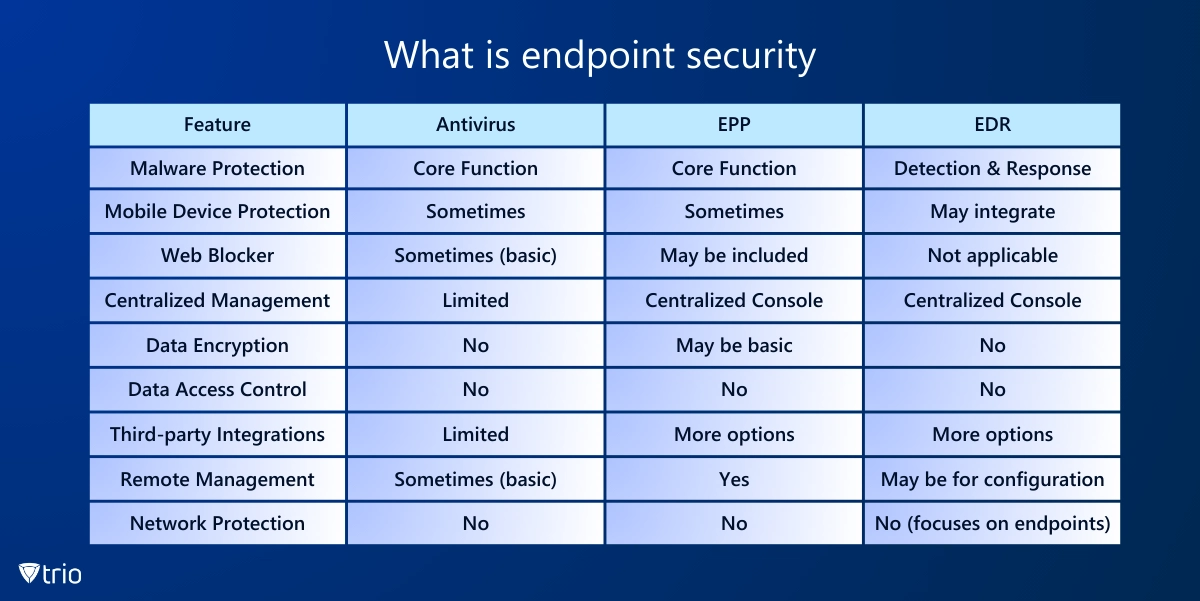
Endpoint Security Software vs. Antivirus Software
The digital landscape is filled with threats, making protecting your organizational devices crucial. Three main lines of defense exist: antivirus software, Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP), and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR).
Antivirus software is the traditional soldier on the frontlines. It excels at identifying and blocking known malware threats using signature-based detection and behavioral analysis. Antivirus software checks file signatures and prevents malware infection. However, antivirus software has limitations. It can struggle against novel threats and lacks the ability to centrally manage security across multiple devices.
EPP builds upon the foundation laid by antivirus software. EPP offers a wider range of preventative measures, including web filtering to block malicious websites and the ability to remotely manage security settings on devices. This centralized management allows for quicker updates and ensures consistent security policies across your network. While EPP is excellent at prevention, it might not catch every single threat that slips through the cracks.
EDR investigates after an incident occurs. It continuously monitors devices for suspicious activity, even if it hasn’t encountered that specific threat before. EDR is like having a security analyst constantly reviewing security footage, identifying malware, and taking action to contain them. While EDR is powerful, it’s not a preventative solution on its own.
The ideal approach combines these methods for a layered defense. Antivirus software provides a baseline shield, EPP strengthens your preventative measures, and EDR equips you to identify and respond to any threats that manage to bypass the first two lines of defense. By combining these tools, you can create a more comprehensive security posture and keep your devices safe from ever-evolving threats.
Ensure Endpoint Protection
The best endpoint protection is not a single solution but is obtained with different steps. Here are some steps a business can take to ensure endpoint protection:
- Implement a Layered Security Approach: This involves combining different security tools to address various threats. Here are some key players:
- Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP): This is the foundation, offering features like anti-malware protection, web filtering, application control, and centralized management.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): This layer focuses on detecting and responding to advanced threats that might bypass EPP. EDR provides continuous monitoring and threat investigation capabilities.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): For businesses with a mobile workforce, MDM is crucial for enforcing security policies, managing applications, and data encryption on mobile devices. One of the MDM solutions that integrates with your EPP and EDR is Trio. Trio simplifies IT management and results in a unified approach.
- Employee Education and Training: Even with the best security tools, human error can be a vulnerability. Regularly train employees on cybersecurity best practices, including:
- Recognizing phishing attempts and social engineering tactics.
- Using strong passwords and practicing good password hygiene.
- Avoiding downloads from untrusted sources.
- Reporting suspicious activity promptly.
- Patch Management: Software vulnerabilities are a common entry point for attackers. Enforce a strict patch management policy to ensure all devices are updated with the latest security patches as soon as they become available.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to add an extra layer of protection in case of a breach.
- Network Segmentation: Segmenting your network can limit the damage caused by a breach by preventing attackers from easily moving laterally across your network.
- Regular Security Audits and Testing: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks and assess your security posture’s effectiveness.
Conclusion: Why Endpoint Security is Essential for Every Business
Endpoint security is no longer a luxury, it’s a necessity. Nowadays, cyber threats are constantly evolving, and businesses of all sizes are potential targets. By implementing a comprehensive endpoint security strategy, you can significantly improve your organization’s overall cybersecurity posture and safeguard your valuable data and assets.
See Trio in Action: Get Your Free Trial Now!
This blog post has equipped you with the knowledge to answer the question “what is endpoint security?” with confidence. We’ve explored the various components that work together to form a robust defense system, the benefits endpoint security offers, and the crucial differences between antivirus software, EPP, and EDR.
Remember, the best endpoint protection isn’t achieved with a single solution. A layered approach that combines EPP for prevention, EDR for advanced threat detection and response, and Mobile Device Management (MDM) for a unified mobile workforce security strategy is key. Don’t forget the importance of employee education and training, regular security audits and testing, and a commitment to data security practices like encryption and patch management. By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks, ensuring business continuity and peace of mind.




